The Last Chapter - A Brief History of Time
- bruce yu
- Dec 27, 2021
- 1 min read
Updated: Jul 31, 2023
Chapter 8: The origin and fate of the universe
Generally accepted history of the universe
Singularity with extremely hot temperature and infinite mass
Big bang
Hydrogen and helium gas break up into smaller clouds, the atoms collide with one another, temperature increases until it is hot enough to convert H to He, stars like our sun are formed
Anthropic principle
Weak AP: the universe is infinite in space and time, the conditions necessary for the development will only be met in certain regions limited in space-time
Strong AP: there are many universes, each with its own initial configuration and its own laws of science ( perhaps)
Sum over histories
A particle does not have just a single history, but it follows every possible paths in space-time
The probability that a particle passes through some particular point is by adding up the waves associated with every possible history that pass through the point
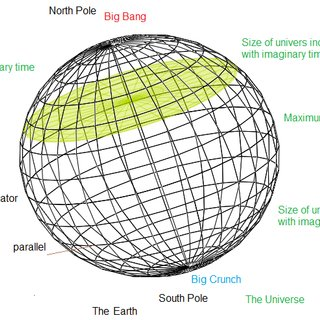
Curved space-time represents the history of the whole universe
Space-time may be like space of the earth, only with 2 more dimensions
No boundaries or edge
The real universe starts at the big bang ( north pole), and ends at the big crunch (south pole)
The imaginary space-time acts the opposite